WeCa: Modular and Flexible Causality Control on the Web
NOTE: There is an update of this Web page here, please visit it. This Web page will be removed soon.
Ajax has allowed JavaScript programmers to create interactive, collaborative, and user-centered Web applications, known as Web 2.0 Applications. These Web applications behave as distributed systems because processors are user machines that are used to send and receive messages between one another. Unsurprisingly, these applications have to address the same causality issues present in distributed systems like the need a) to control the causality between messages sent and responses received and b) to react to distributed causal relations. JavaScript programmers overcome these issues using rudimentary and alternative techniques that largely ignore the distributed computing theory. In addition, these techniques are not very flexible and need to intrusively modify these Web applications. We study how causality issues affect these applications and present WeCa, a practical library that allows for modular and flexible control over these causality issues in Web applications. In contrast to current proposals, WeCa is based on aspects and stateful aspects, message ordering strategies, and vector clocks. We illustrate WeCa in action with several practical examples from the realm of Web applications. For instance, we analyze the flow of information in Web applications like Twitter using WeCa.
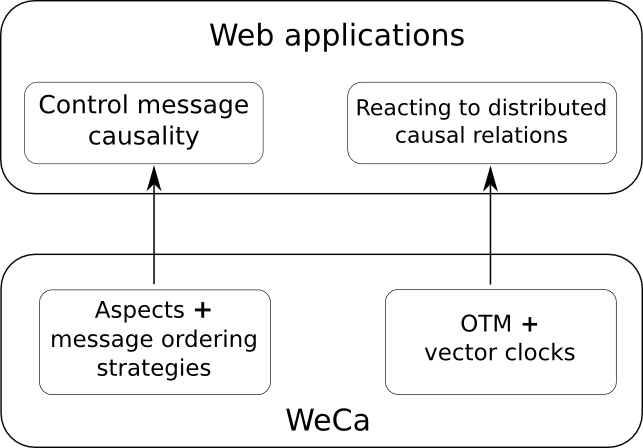
The figure shows the needs of causality of Web applications and how WeCa proposes to satisfy these needs. In this Web site, you can find examples of these needs: